Free Pronoun Finder Tool
Find and highlight all types of pronouns in your text with our free online pronoun identifier. Instantly discover personal, possessive, demonstrative, and indefinite pronouns with color-coded highlighting. Perfect for students, teachers, ESL learners, and writers aiming to improve clarity and avoid repetition.
Try these examples:
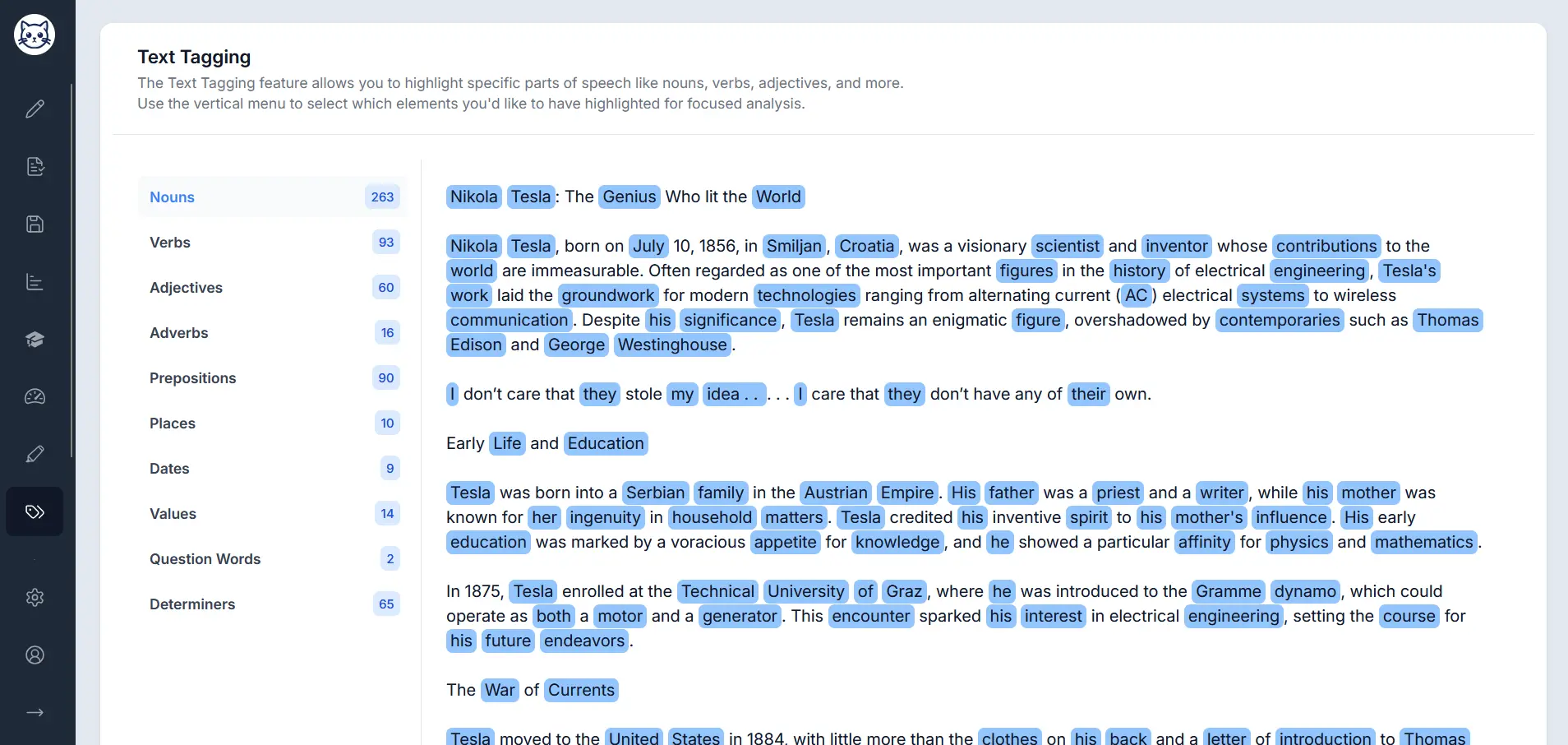
Advanced Parts of Speech Analysis
Go beyond basic pronoun detection with Gorby's text tagging feature. Analyze nouns, verbs, adjectives, and all parts of speech with comprehensive statistics.
What Are Pronouns?
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun or noun phrase. Common examples include he, she, it, they, and I. Pronouns help make language less repetitive and more efficient by substituting for a noun that has already been mentioned, which is known as the pronoun's antecedent. For instance, instead of saying "Sarah loves fashion, so Sarah wants to go to fashion school," you can say "Sarah loves fashion, so she wants to go to fashion school."
By using a pronoun, you make your writing clearer and more concise. Our pronoun finder tool is built to help you identify and understand the different types of pronouns in any text, improving your grammatical accuracy and writing style.
Why Pronouns Matter in Writing
Pronouns are fundamental building blocks of clear communication. They streamline sentences and improve readability, but their importance extends beyond just avoiding repetition. Proper pronoun usage helps you:
- Improve Sentence Flow: Using pronouns creates smoother, more natural-sounding sentences, preventing the clunky effect of repeating the same noun.
- Enhance Clarity: When used correctly, pronouns make it easy for the reader to follow who or what you are talking about without needing constant reminders.
- Add Variety to Language: Switching between nouns and pronouns makes your writing more dynamic and engaging for the reader.
- Show Respect and Inclusion: Using a person's correct pronouns (e.g., she/her, he/him, they/them) is a fundamental way to show respect for their identity.
Key Types of Pronouns
Pronouns come in several forms, each with a specific grammatical function. Our pronoun locator can distinguish these types to help you analyze sentences more effectively. Here are some of the most common categories.
Personal Pronouns
Refer to a specific person or thing.
Examples:
Subject: I, you, he, she, it, we, they
Object: me, you, him, her, it, us, them
Possessive Pronouns
Indicate ownership or possession.
Examples:
Independent: mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs
Demonstrative Pronouns
Point to specific people or things.
Examples:
this, that, these, those
Quick Tip: How to Find a Pronoun in a Sentence
To easily identify pronouns, look for words that are replacing nouns. If you can substitute a person's name (like "Maria") or an object's name (like "the ball") for the word, it is likely a pronoun.
- Look for substitutes: Find words that stand in for a noun that was mentioned earlier.
- Check the function: Does the word act as the subject or object of the verb? Pronouns fill these roles just like nouns do.
- Identify the antecedent: The antecedent is the noun the pronoun refers to. Finding it confirms the word is a pronoun (e.g., in "The dog wagged its tail," "dog" is the antecedent).
- Use our pronoun finder: Let our tool automatically highlight all pronouns and classify them for you!
Example Sentence Analysis
"Maria knew the book was hers, but she let David read it because this is what friends do for each other."
she, it = Personal pronouns (referring to Maria and the book)
hers = Possessive pronoun (shows ownership)
this = Demonstrative pronoun (points to the concept of sharing)
each other = Reciprocal pronoun (refers to a mutual relationship)
This sentence uses multiple types of pronouns to avoid repeating "Maria," "the book," and "David," making it flow more naturally while maintaining clear meaning.
Types of Pronouns with Examples
Understanding the different types of pronouns helps you analyze writing more effectively. Our pronoun finder uses color-coding to help you identify each type instantly.
Personal Pronouns
Refer to specific people, groups, or things
Personal pronouns are the most common type. They change form based on their role in the sentence (subject or object) and their point of view (first, second, or third person).
Subject Pronouns
Perform the action of the verb:
Example:
"She went to the library."
Object Pronouns
Receive the action of the verb:
Example:
"The teacher gave the book to him."
Possessive Pronouns
Indicate ownership
These pronouns show that something belongs to someone. They stand alone and don't modify a noun.
Example:
"The red car is mine."
Demonstrative Pronouns
Point to specific things
These pronouns identify specific nouns, indicating their proximity (near or far) to the speaker.
Example:
"That is the house I was talking about."
Relative Pronouns
Connect a clause to a noun
These pronouns introduce a dependent clause and connect it to a noun that came before it.
Example:
"The student who won the award was very talented."
Interrogative Pronouns
Used to ask questions
These pronouns are used at the beginning of a question to inquire about a person, place, or thing.
Example:
"What is your favorite color?"
Other Pronoun Categories
Indefinite Pronouns
Refer to non-specific people or things.
Examples: all, any, anyone, everyone, somebody, nothing, several, some
Reflexive Pronouns
Refer back to the subject of the sentence.
Examples: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, themselves
Reciprocal Pronouns
Indicate a mutual action or relationship.
Examples: each other, one another
Quick Reference: Pronoun Types Summary
Personal
Refers to people/things
I, she, him, they
Possessive
Shows ownership
mine, yours, hers
Demonstrative
Points to something
this, that, these
Interrogative
Asks a question
who, what, which
Who Benefits from Our Pronoun Finder?
From mastering grammar to refining professional writing, our pronoun identifier is a vital tool for anyone working with text. It helps clarify meaning, improve flow, and ensure grammatical accuracy.
Students
Strengthen your writing by ensuring clear pronoun-antecedent agreement and avoiding repetition. Perfect for checking essays, grammar homework, and preparing for tests.
ESL Learners
Pronoun cases and agreement can be tricky. This tool helps you visually learn the correct forms and usage patterns, accelerating your journey to fluent English writing.
Teachers & Educators
Create engaging lessons on pronoun types and functions. Use our tool to visually demonstrate concepts, generate examples for quizzes, and quickly assess student writing for clarity and correctness.
Writers & Content Creators
Craft clearer and more compelling prose by auditing your pronoun usage. This tool helps you spot ambiguous references and maintain a consistent narrative voice, ensuring your message is always clear.
Ready to Write with Clarity?
Join thousands of students, writers, and educators who use our pronoun finder to strengthen their grammar and improve their writing.
Try the Pronoun Finder ToolWriting with Pronouns
Effective pronoun usage is key to clear, professional writing. Learn how to avoid common errors and use pronouns to enhance readability and style.
Common Pronoun Mistakes to Avoid
Pronoun-Antecedent Agreement
A pronoun must agree in number with its antecedent (the noun it replaces).
Incorrect: "If a student wants to succeed, they should study."
Correct: "If students want to succeed, they should study."
(Note: Using singular "they" is now widely accepted to avoid gendered language.)
Vague Pronoun Reference
Ensure every pronoun clearly refers to a single, specific antecedent to avoid confusion.
Unclear: "When Maria gave her mom the gift, she was very happy." (Who is "she"?)
Clear: "Maria's mom was very happy when she received the gift."
Choosing the Correct Case: Subject vs. Object
Use subject pronouns (I, he, she, we, they) when the pronoun is the one performing the action. Use object pronouns (me, him, her, us, them) when the pronoun is receiving the action.
In Compound Subjects/Objects
Incorrect: "Me and him went to the store."
Correct: "He and I went to the store."
Tip: Test by removing the other person. You wouldn't say "Me went to the store."
After Prepositions
Incorrect: "This is a secret between you and I."
Correct: "This is a secret between you and me."
Tip: Pronouns following prepositions (like 'between', 'for', 'with') should always be object pronouns.
Commonly Confused Words
Who vs. Whom
Use who as a subject (he/she).
Use whom as an object (him/her).
"Who is coming?" (He is.)
"To whom did you give the letter?" (to him.)
Its vs. It's
Its is a possessive pronoun.
It's is a contraction of "it is" or "it has".
"The dog wagged its tail."
"It's a beautiful day."
Their vs. They're vs. There
Their shows possession.
They're is a contraction of "they are".
There refers to a place.
"It is their car."
"They're running late."
"Put the book over there."
That vs. Which
That introduces essential information.
Which introduces non-essential information (usually set off by commas).
"I like the car that is red." (essential)
"The car, which is red, is fast." (non-essential)
Explore More Grammar & Text Tools
Enhance your writing and grammatical understanding with our comprehensive collection of free text analysis tools.
Preposition Finder
Identify relational words that connect sentence elements to clarify meaning and context.
Find PrepositionsNoun Finder
Locate subjects, objects, and ideas by highlighting all nouns in your document.
Find NounsAdjective Finder
Identify descriptive words to improve the imagery and vividness of your text.
Find AdjectivesWord Counter
Track the word count of your document in real-time to meet writing requirements.
Count WordsFlesch Reading Ease
Test how easy your text is to read using the popular Flesch readability formula.
Check ReadabilitySpeaking Time Calculator
Estimate how long your text will take to speak, perfect for speeches and presentations.
Calculate Speaking TimeResources & Further Reading
To learn more about pronoun rules and usage, these authoritative grammar guides offer detailed explanations and practical examples.
Purdue Online Writing Lab (OWL)
A comprehensive academic resource covering pronoun-antecedent agreement, pronoun case, and how to avoid vague references in your writing.
Visit Purdue OWL on Pronouns →Grammarly Handbook
A clear and accessible guide explaining the different types of pronouns with easy-to-understand examples and tips for avoiding common mistakes.
Read the Grammarly Guide →Merriam-Webster Dictionary
Provides clear definitions for each type of pronoun and discusses modern usage, including the evolution and acceptance of the singular "they."
Explore Merriam-Webster on Pronouns →Ready for Professional Text Analysis?
Take your writing analysis to the next level with Gorby's comprehensive text analyzer. Get advanced features, real-time feedback, and detailed insights into your writing.
Advanced Text Analysis
Complete parts of speech tagging, readability scores, and writing insights
Real-Time Feedback
Get instant suggestions as you type to improve your writing style
Privacy Focused
All analysis happens locally - your text never leaves your device
Free to try • No signup required • Works in your browser
