Free Conjunction Finder Tool
Instantly find and highlight all types of conjunctions in your text. Our free online tool identifies coordinating (FANBOYS), subordinating, and correlative conjunctions, helping you analyze and improve your sentence structure. Perfect for students, teachers, and writers aiming for clarity and precision.
Try these examples:
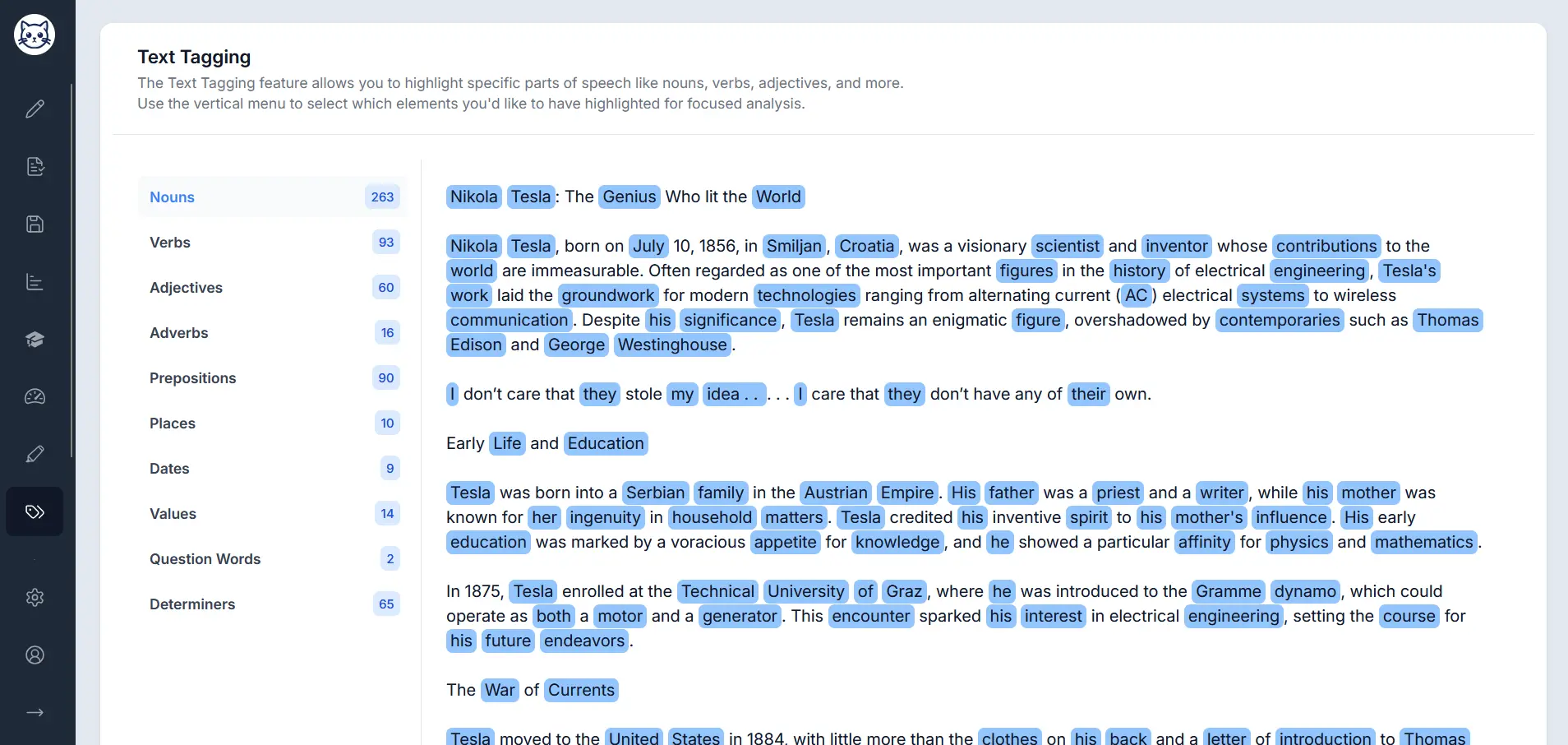
Advanced Parts of Speech Analysis
Go beyond basic conjunction detection with Gorby's text tagging feature. Analyze nouns, verbs, adjectives, and all parts of speech with comprehensive statistics.
What Are Conjunctions?
Conjunctions are words that act as connectors in sentences. They link words, phrases, and clauses, serving as the glue that holds your ideas together. Common examples include and, but, or, and because. Without conjunctions, you would be forced to write in a series of short, simplistic sentences, making your text choppy and disconnected.
By learning how to find and use conjunctions effectively, you can build more complex, elegant, and readable sentences. Our conjunction finder tool is designed to help you identify these crucial connectors and understand their role in constructing meaningful relationships between different parts of a sentence.
Why Conjunctions Matter in Writing
Conjunctions are essential for creating fluid, sophisticated prose. They allow you to move beyond simple statements and express complex relationships between ideas, such as contrast, cause and effect, or sequence. Proper use of conjunctions helps you:
- Connect Related Ideas: Join two or more thoughts into a single, cohesive sentence to show how they are related.
- Improve Sentence Variety and Flow: Create a mix of simple, compound, and complex sentences to make your writing more engaging and less monotonous.
- Establish Clear Relationships: Show readers exactly how ideas relate, whether it's through addition (and), contrast (but), or reason (because).
- Avoid Choppy Sentences: Combine short, abrupt sentences into longer, more graceful ones that are easier to read and understand.
The Three Main Types of Conjunctions
Our conjunction identifier categorizes these connectors into three main types. Understanding their different functions is key to mastering sentence structure.
Coordinating
Connect grammatically equal elements (words, phrases, or independent clauses).
FANBOYS:
For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet, So
Subordinating
Connect an independent clause to a dependent (subordinate) clause.
Examples:
because, since, although, while, if, until, after
Correlative
Pairs of conjunctions that work together to join elements.
Examples:
either/or, neither/nor, not only/but also, both/and
Quick Tip: How to Find a Conjunction
To spot conjunctions, look for words that join parts of a sentence. Each type has its own clue:
- Memorize FANBOYS: For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet, So. If you see one of these joining two complete sentences, it's a coordinating conjunction.
- Look for Dependent Clause Starters: Words like 'because', 'while', 'if', and 'although' often signal the start of a dependent clause, making them subordinating conjunctions.
- Spot the Pairs: Correlative conjunctions always come in pairs. If you find an 'either', look for the 'or'. If you see 'not only', find the 'but also'.
- Use our conjunction finder: Let our tool instantly highlight and categorize all conjunctions for you!
Example Sentence Analysis
"Not only do I want to go to the party, but I also need to finish my work before I can leave, so I'll be late."
not only / but also = Correlative Conjunction (connects two related ideas)
before = Subordinating Conjunction (introduces the dependent clause "before I can leave")
so = Coordinating Conjunction (connects the two independent clauses)
This example demonstrates how different conjunctions work together to create a single, complex sentence that logically connects multiple ideas and conditions.
Types of Conjunctions with Examples
Conjunctions are classified into three main groups based on how they connect words and clauses. Our tool helps you distinguish between them to better understand sentence structure.
Coordinating Conjunctions
Connect grammatically equal elements
Coordinating conjunctions join words, phrases, and independent clauses that are of equal importance. There are only seven of them, which can be remembered with the acronym FANBOYS.
The FANBOYS Acronym
Example:
"She wanted to go to the beach, but it was raining."
When a coordinating conjunction connects two independent clauses (complete sentences), it is usually preceded by a comma.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Join a dependent clause to an independent clause
Subordinating conjunctions introduce a dependent clause (a clause that cannot stand alone as a sentence) and connect it to an independent clause. They show a relationship of time, reason, condition, or contrast.
Common Examples
Example in a Sentence
"He did not go to the park because it was raining."
"Although it was raining, he went to the park."
Comma Rule:
If the dependent clause comes before the independent clause, use a comma to separate them. If it comes after, no comma is needed.
Correlative Conjunctions
Pairs of conjunctions that work together
Correlative conjunctions are pairs that join balanced words, phrases, or clauses. The elements they connect must be grammatically equal, a rule known as parallel structure.
Common Pairs
either / or
neither / nor
not only / but also
both / and
whether / or
Example:
"You can have either tea or coffee."
"He is not only a great student but also a talented athlete."
Notice that "a great student" and "a talented athlete" are both noun phrases, maintaining parallel structure.
Quick Reference: Conjunction Types Summary
Coordinating
Joins equal parts
and, but, or (FANBOYS)
Subordinating
Joins dependent to independent clause
because, if, while
Correlative
Works in pairs
either/or, not only/but also
Who Benefits from Our Conjunction Finder?
From constructing complex sentences to improving readability, our conjunction identifier is an essential tool for anyone who wants to write with precision and clarity.
Students
Improve your essay writing by learning to create varied and complex sentences. This tool helps you identify how ideas are linked, avoid run-on sentences, and master comma usage.
ESL Learners
Mastering sentence connectors is key to fluency. This tool helps you see how different conjunctions create relationships like cause ('because'), contrast ('although'), and condition ('if').
Teachers & Educators
Create engaging lessons on sentence structure and syntax. Use the tool to highlight different conjunction types, create grammar exercises, and demonstrate how to build compound and complex sentences.
Writers & Content Creators
Craft elegant and persuasive prose by analyzing your sentence structure. Use the tool to identify overuse of simple conjunctions ('and', 'but') and find opportunities to create more sophisticated sentence patterns.
Ready to Build Better Sentences?
Join thousands of users who rely on our conjunction finder to improve their writing flow, clarity, and grammatical precision.
Try the Conjunction FinderWriting with Conjunctions
Mastering conjunctions is about more than just knowing the words; it's about understanding how to use them to control sentence structure, pace, and clarity.
Comma Usage with Coordinating Conjunctions
A common source of confusion is when to use a comma before a coordinating conjunction (For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet, So). The rule is simple:
Use a Comma
When the conjunction joins two independent clauses (clauses that could be separate sentences).
"The sun was setting, so we decided to head home."
Do Not Use a Comma
When the conjunction joins two words, phrases, or a dependent clause.
"She likes to read and listen to music."
Building Complex & Compound Sentences
Conjunctions are the primary tools for moving beyond simple sentences. Use them to create variety and show sophisticated relationships between ideas.
Creating Compound Sentences
Join two independent clauses with a coordinating conjunction (FANBOYS) to give them equal weight.
Simple: The team practiced hard. They lost the game.
Compound: "The team practiced hard, but they lost the game."
Creating Complex Sentences
Join an independent clause with a dependent clause using a subordinating conjunction to show an unequal relationship (e.g., cause/effect, time).
Simple: She studied for the test. She passed with a high score.
Complex: "Because she studied for the test, she passed with a high score."
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Run-On Sentences
This happens when you join two independent clauses with no conjunction or punctuation.
Incorrect: "It was a beautiful day we went to the park."
Correct: "It was a beautiful day, so we went to the park."
Comma Splices
This is when you join two independent clauses with only a comma, which is not strong enough.
Incorrect: "The music was loud, the crowd was energetic."
Correct: "The music was loud, and the crowd was energetic."
Explore More Grammar & Writing Tools
Improve your sentence structure, clarity, and overall writing with our full suite of free text analysis tools.
Pronoun Finder
Identify pronouns to check for clear antecedents and improve sentence flow.
Find PronounsPreposition Finder
Locate prepositions and prepositional phrases to analyze sentence structure and clarity.
Find PrepositionsSentence Counter
Count sentences and analyze average sentence length to improve readability and pace.
Count SentencesParagraph Counter
Easily count the number of paragraphs to check the structure of your document.
Count ParagraphsFlesch-Kincaid Grade Level
Calculate the U.S. grade level of your text to ensure it's accessible to your audience.
Calculate Grade LevelKeyword Density
Analyze keyword frequency and density for SEO and content optimization.
Analyze KeywordsResources & Further Reading
To deepen your understanding of how to use conjunctions effectively, these grammar resources provide expert guidance and detailed examples.
Grammarly Handbook
A clear and accessible overview of the three types of conjunctions, with helpful examples and tips for avoiding common errors like comma splices.
Read the Grammarly Guide →Khan Academy
Offers video lessons and practice exercises on coordinating and subordinating conjunctions, perfect for visual learners and students.
Learn on Khan Academy →Ready for Professional Text Analysis?
Take your writing analysis to the next level with Gorby's comprehensive text analyzer. Get advanced features, real-time feedback, and detailed insights into your writing.
Advanced Text Analysis
Complete parts of speech tagging, readability scores, and writing insights
Real-Time Feedback
Get instant suggestions as you type to improve your writing style
Privacy Focused
All analysis happens locally - your text never leaves your device
Free to try • No signup required • Works in your browser
